WE, THE PEOPLE OF INDIA,
having solemnly resolved to constitute India
into a SOVEREIGN SOCIALIST SECULAR DEMOCRATIC
REPUBLIC and to secure to all its citizens:
JUSTICE, social, economic and political;
LIBERTY of thought, expression, belief, faith and worship;
EQUALITY of status and of opportunity;
and to promote among them all
FRATERNITY assuring the dignity of the individual and
the unity and integrity of the Nation;
IN OUR CONSTITUENT ASSEMBLY this 26th day of
November, 1949, do HEREBY ADOPT, ENACT AND GIVE
TO OURSELVES THIS CONSTITUTION
What are you feeling right now? The feelings that the Preamble of our Constitution evokes, are not easy to put into words. The emotions and conviction with which it was written were honest, untainted, and unlayered. Perhaps the idealistic values mentioned in the Preamble came naturally to the author. Let’s revisit them today.
Our Preamble In Nutshell:
The Preamble sets forth the basic underlying principles and the concepts on which our Constitution is framed, which is a testament to the sound ideals and judiciary views of Constitution Framers’ minds. When the framers started drafting the Constitution, they had high standards and postulates in mind which would forge the nation’s path towards glory and stability. It is said, when the members were signing the historic document it was drizzling outside which is considered a good omen, and it turned out to be so.
In a nutshell, the Preamble is an introduction to the statute which helps in understanding the legislative intent. The Preamble to the Indian Constitution sets forth the five characteristics and four objectives, which include the concepts of Sovereign, Socialist, Secular, Democratic Republic and the objectives of Justice, Liberty, Equality and Fraternity. All the above grand characteristics enshrined in our Constitution, perfectly summarise the essence of the core values of India; it highlights the prevailing fundamentals in the socio-political context and fulfills the needs and demands of the citizens. Hence, the essence of the Constitution lies in the words ‘We The People’, which implies that the ultimate source of the Constitution is the will of the people. Let’s understand our Constitution before we move on to the concepts and objectives, which are its guiding principles.
Introduction to the Indian Constitution
Every country has a constitution in place which outlines and aggregates the country’s fundamental principles and government structure. In India, the constitution makes up the core of the country’s existence. Moreover, not only does it robustly bind the country’s diversity and distinct cultures, but also empowers and safeguards the rights and liberties of the citizens while maintaining an effective balance between the organs of the government. The doctrines laid, limit the concentration of power into the hands of a single governing body and keep a check on its misuse by authorities. The constitution also aids a consensus amid parties when there is a disparity in thoughts and opinions. The set of rules reflect the expectations India’s citizens have from the country’s leaders. They include the type of governance and the ideals the country should uphold. The core values of the Indian Constitution, that constitute its spirit, are expressed in a number of articles and provisions.
Our constitution is one that was crafted with great foresight. The framers of our Constitution were careful in drafting its amendment provisions as they were highly aware of the fact that the Constitution that they were drafting could neither be too rigid or too flexible. Owing to their meticulous planning, presently, we have three kinds of provisions in the Constitution. There are some provisions that have the room for amendments by a simple majority; and they are not considered to be constitutional amendments in the most proper sense of the term. Most importantly, there is no provision in the Constitution which is expressly kept beyond reach of the Parliament. It was vital for the framers to guarantee that future Parliaments did not face obstacles in amending provisions of the Constitution that would pose genuine difficulties to the country. No matter what, at the end of the day, we must remember that constitutionalism is a work in progress and is constantly adapting. The mark of a good constitution is its ability to change with time.
The Framers of the Constitution:
Before getting to the guiding values of the Indian Constitution, it is essential to understand a little more about the Indian Constitution.
On 26th November 1949, the Constituent Assembly of India adopted India’s Constitution, which came into effect on 26 January 1950. The Indian Constitution is considered to be the most elaborated and longest in the world, for a sovereign nation with 145,000 English word count, which easily exceeds word length of most novels. During the sanctioning, it had 395 articles in 22 parts and 8 schedules.
The Constitution was framed by the Constituent Assembly of India, established by the members of the provincial assemblies elected by the people of India. Dr Sachidananda Sinha was the first president of the Constituent Assembly, who was later succeeded by Dr Rajendra Prasad. The then chairman of the Drafting Committee, Dr B. R. Ambedkar, is considered to be the chief architect of the Indian Constitution which provides a comprehensive and dynamic framework to guide and govern the country. Dr B. R. Ambedkar is believed to have studied the constitutions of about 60 countries before preparing the statute of the world’s largest democracy, India!
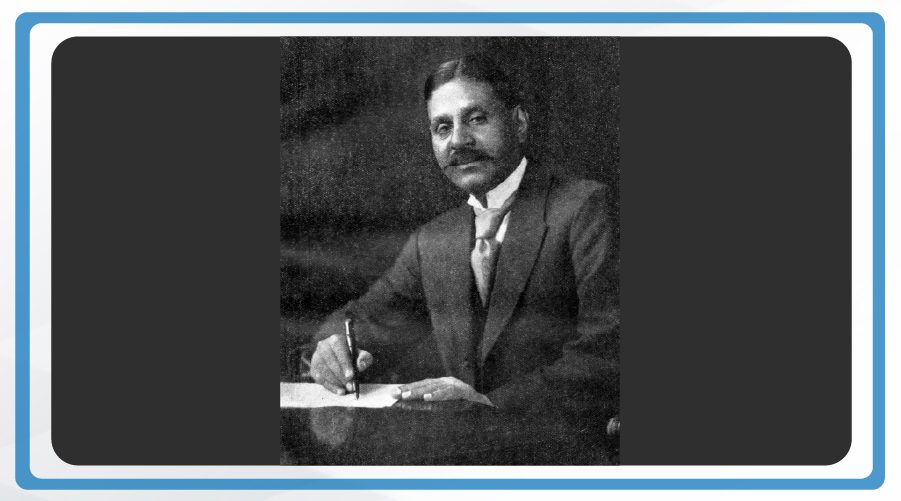

Dr Sachidananda Sinha
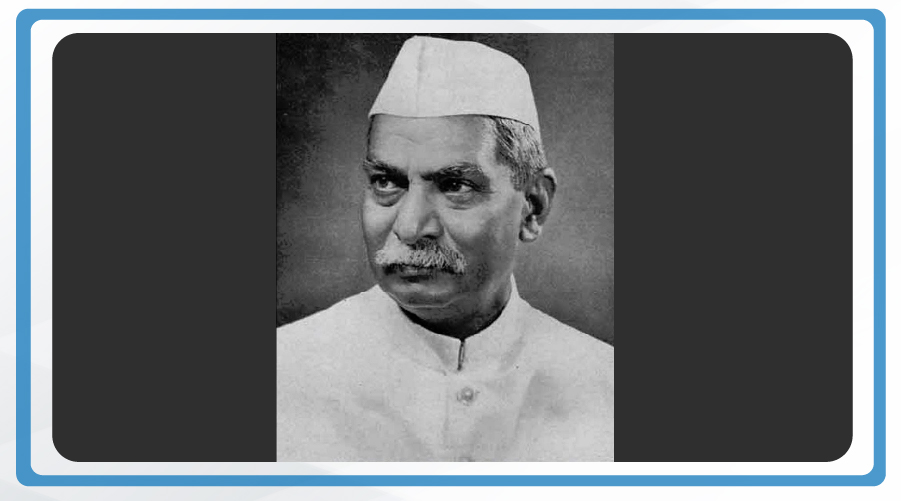

Dr. Rajendra Prasad
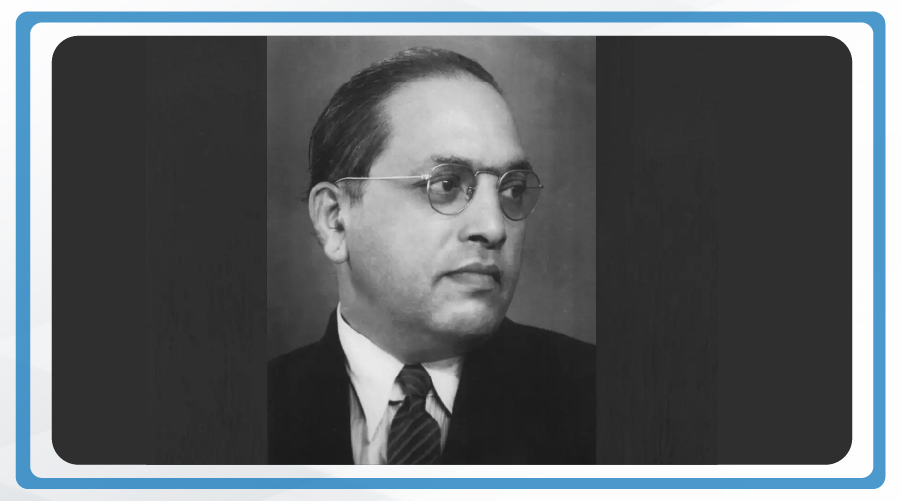

Dr. B. R. Ambedkar, Father of Indian Constitution
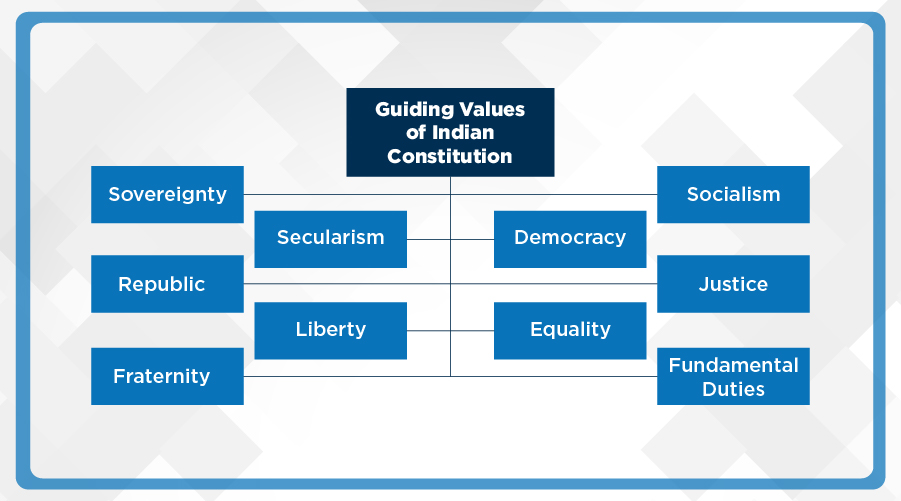
The Core Values That Guide the Nation:
“To no one will we sell, or deny, or delay, rights or justice.”
There are ten values in the Indian Constitution, that guide the nation and its citizens:
1.Sovereignty
The word ‘Sovereignty’ comes from the Latin word ‘Superanus’ which means supreme. In the words of John Austin, Sovereignty means, “A specific authority in a particular society, or those who are not loyal to any other authority but have the general loyalty of all the people of that society, then that superior authority is called sovereign, and the society with that sovereign authority is an independent and political society.”
The feature of sovereignty, bestows dignity and recognition to a country on an international scale. In a complete sovereign nation, the government bodies and constitutional authorities derive their power only from the people. India is a sovereign country with complete political freedom and supreme authority. It implies that India is internally all-powerful and externally free. It is free to determine for itself without any external interference (either by any country or individual), and nobody is there within to challenge its authority. This feature of sovereignty gives India the dignity of existence as a nation in the international community.
2.Socialism
Socialism is a system in which every person in the community has an equal share of the various production, distribution, and exchange of resources. Socialism has been made a constitutional value to promote social change and transformation to end all forms of inequalities. Our Constitution directs the governments and the people to ensure a planned and coordinated social development in all fields. It refers to preventing the concentration of wealth and power in a few hands.
3.Secularism
India is one of the largest secular countries in the world as it is the home and birthplace of major religions of the world. Secularism implies that India is not guided by any religion or any religious considerations, allowing all citizens to profess, preach and practise any religion they follow. At the same time, it ensures that the state does not have any religion of its own. The Indian Constitution strictly prohibits any discrimination on the grounds of religion.
4.Democracy
Democracy, as a form of government, obtains its authority from the will of the people. It represents governance that the people elect, and the elected representatives remain accountable to the people.
Democracy contributes to stability, continuous progress in society, and it secures peaceful political change. It allows dissent and encourages tolerance. It is based on the principles of the rule of law, inalienable rights of citizens, independence of the judiciary, free and fair elections and freedom of the press. Democracy is futuristic terminology with numerous aspects like participatory democracy, citizens’ assemblies, self-governing city-states, referendums, e-democracy, intergenerational rights, participatory budgeting and liquid democracy.
5.Republic
India is a republic nation, and the most important symbol of this is the President, who is elected and not selected based on heredity as seen in a monarchy. The value of ‘republic’ in the Indian Constitution strengthens and substantiates democracy where every citizen is equally eligible to be elected as the Head of the State. Political equality is the chief message of this value.
6.Justice
Justice refers to fairness and can also mean different things to different people. Justice is an essential value under law and politics.
Social justice is the notion that everyone deserves equal economic, political, and social opportunities irrespective of race, gender, or religion. Distributive justice indicates equitable allocation of assets in society. Environmental justice is the fair treatment of all people concerning environmental burdens and benefits. Restorative or corrective justice seeks to make whole those who have suffered unfairly. Retributive justice seeks to punish wrongdoers objectively and proportionately. Procedural justice refers to implementing legal decisions following fair and unbiased processes.
Living in a democratic system, we often find that there are many cases where not only social and economic justice but also political justice is denied. This is the very reason behind the constitution-makers including social, economic and political justice as constitutional values. By doing so, they have stressed that the political freedom granted to Indian citizens has to be instrumental in creating a new social order based on socio-economic justice. This idea of a just and egalitarian society remains as one of the principal values of the Indian Constitution.
7.Liberty
Liberty is the ability to do as one pleases. In politics, it indicates the state of being free within society from control or oppressive restrictions imposed by authority on one’s way of life, behaviour, or political views.
The Preamble prescribes liberty of thought, expression, belief, faith and worship as one of the core values that have to be assured to every member of all the communities.
8.Equality
Equality is as vital as all the other constitutional values. Equality indicates the fair and just treatment of all members. The Indian Constitution ensures equality for every citizen. Inequality in any form present in our country and society has been prohibited. Equality is reflected explicitly in the Preamble and is therefore held as an essential value.
9.Fraternity
Fraternity indicates a brotherhood formed around common goals and aspirations. The Preamble also mentions fraternity as an essential value in the Indian Constitution. In the absence of fraternity, a plural society like India stands divided. Therefore, to give meaning to all the ideals like justice, liberty and equality, the Preamble emphasises fraternity. Fraternity is essential to ensure the dignity of the individual, which is another significant value of the Indian Constitution. It is necessary to ensure the dignity of every individual and their equal participation, without which democracy cannot function.
Another value promoted by fraternity is unity and integrity of the nation. To keep the country’s independence intact, the unity and integrity of the nation are essential. The Indian Constitution expects all the citizens of India to uphold and protect the unity and integrity of the country.
10.Fundamental Duties
The Indian Constitution states some duties that need to be performed by the citizens. These duties are not enforceable in the court of law but are still inevitable in nature. Fundamental duties have greater importance because these reflect specific values like patriotism, nationalism, humanism, environmentalism, harmonious living, and gender equality.
The Essence Of The Ten Values Of The Constitution :
Ethical values are those principles or values that determine what is right and what is wrong in different situations. Values such as integrity, transparency, accountability, impartiality, public welfare and equity are considered to be the guiding principles of the Indian Constitution. During the time of its creation, the ten values were curated in such a way that the citizens of India could feel empowered. Despite being nearly 7 decades old, the robust Indian Constitution comprises all such values that are universal and democratic and that reflect the modern age we live in.
Sovereignty was incorporated in the Preamble so as to provide supreme power to the Government and it is the backbone of our Indian Constitution as it protects the authority of the people. Secularism is vital to India, a land of rich cultural differences so that there might be harmony between different communities and religions. Democracy is an ancient concept that was being followed by many South Indian rulers and it is used throughout India to allow people to have the power to govern. Our society, based on socialism, intends to promote equality amongst people so as to ensure the welfare of people. Since, elections are the fairest way of establishing our leaders, India was therefore established as a republic so that people could have the power to elect their own representatives and to ensure that there are no hereditary rulers.
If we look at our constitution closely, we can observe how The Constitution of India was very dynamically created by our lawmakers to ensure justice, liberty and fraternity among citizens. There are tons of salient features that make our Indian Constitution special. Our lawmakers have ensured to take all the factors into account and try to accommodate all the differences that exist within our country. Hence, the Constitution and various rights present in the Constitution will always be the guardian of our citizens.
The Frameworks Binding Our Nation:
As we can clearly see, the values enshrined in the Indian Constitution are wholly based on a strong ethical foundation. These values enlisted in the Indian constitution aim to inspire the citizens and make the Indian society move towards an ethical approach through the promotion of the spirit of tolerance and respecting the unity in diversity present in India.
Our constitution may be young, but it has gone through some tremendous changes over the last seven decades. What is even more awe-inspiring is that it has demonstrated remarkable resilience by surviving all assaults on it. Most citizens may not know of all the procedural details associated with this lengthy and imperfect document, but they do know the crux of it. The citizens are not governed by the impulses of careless political avarice, but by the very words of the Constitution. This is worth celebrating.
The National Constitution Day, also known as ‘Samvidhan Divas’, is celebrated to commemorate the adoption of India’s Constitution and promote Constitutional values among citizens. It is also known as National Law Day.
As Dr B. R. Ambedkar aptly states, “The Constitution is not a mere lawyer’s document, it is a vehicle of life, and its spirit is always the spirit of the age!” This Constitution Day, let us understand and embrace the guiding values of the Indian Constitution!
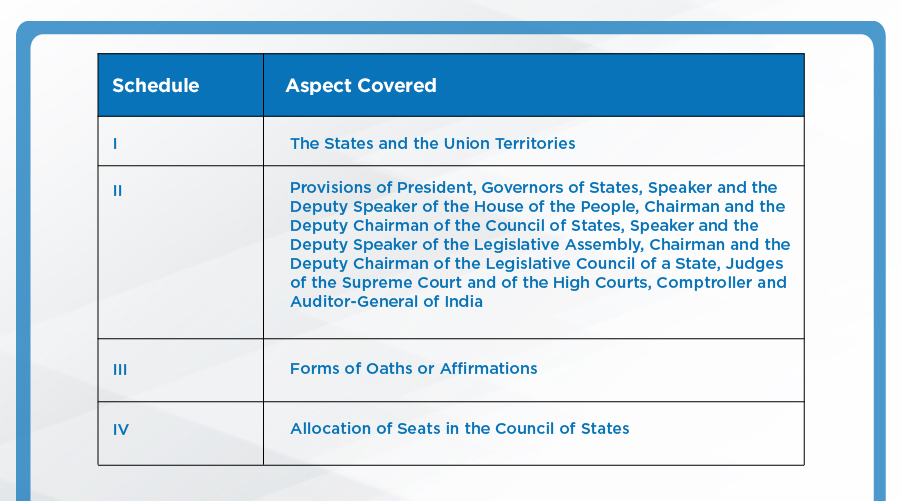
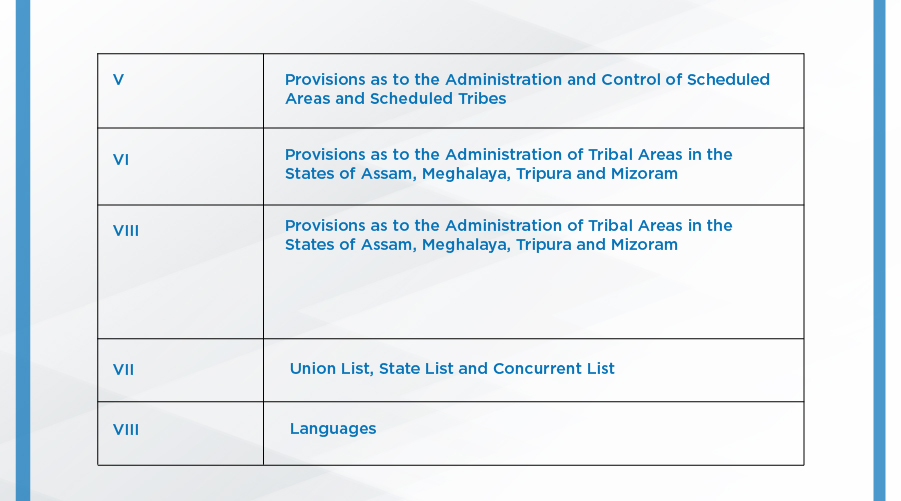
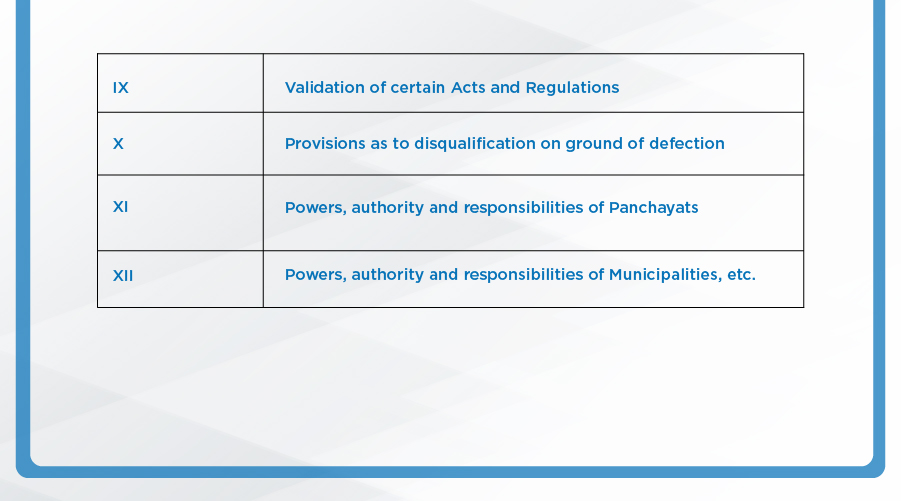
APPENDIX:
Parts of the Indian Constitution:
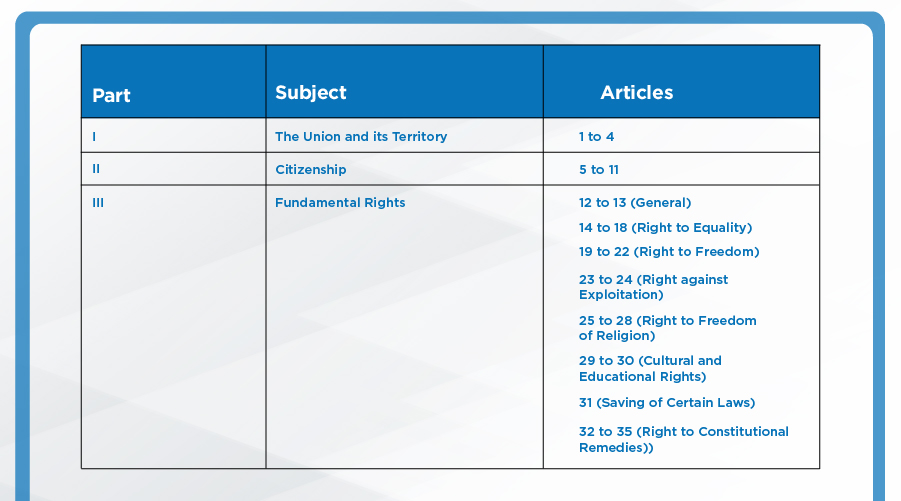
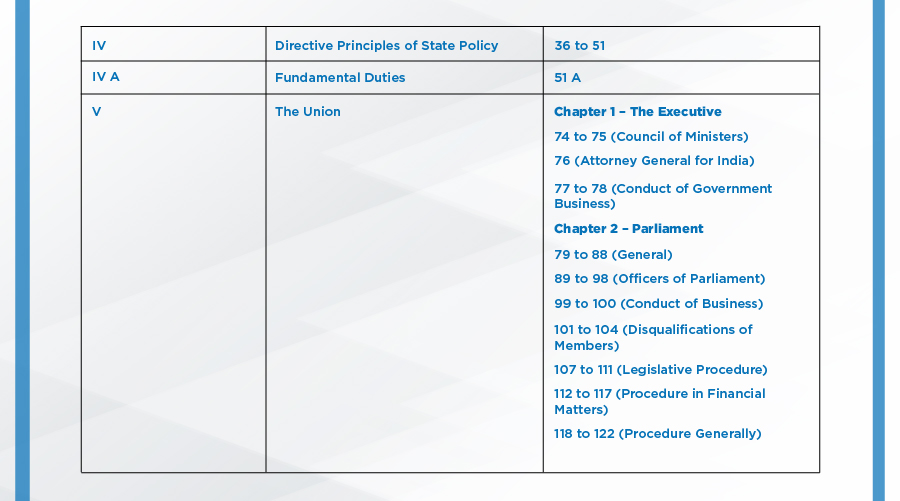
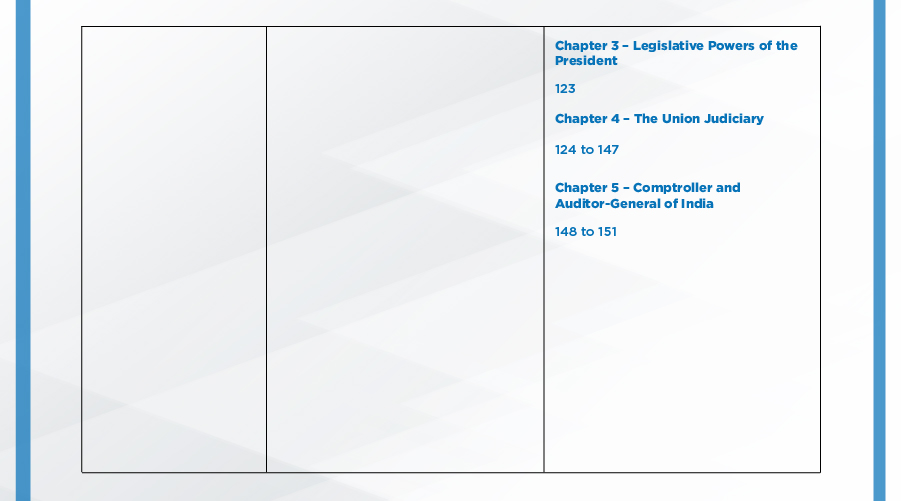

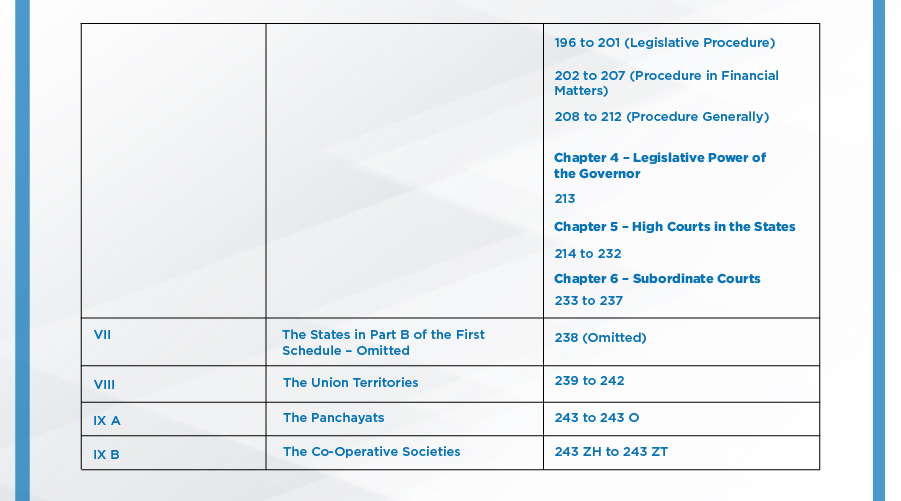
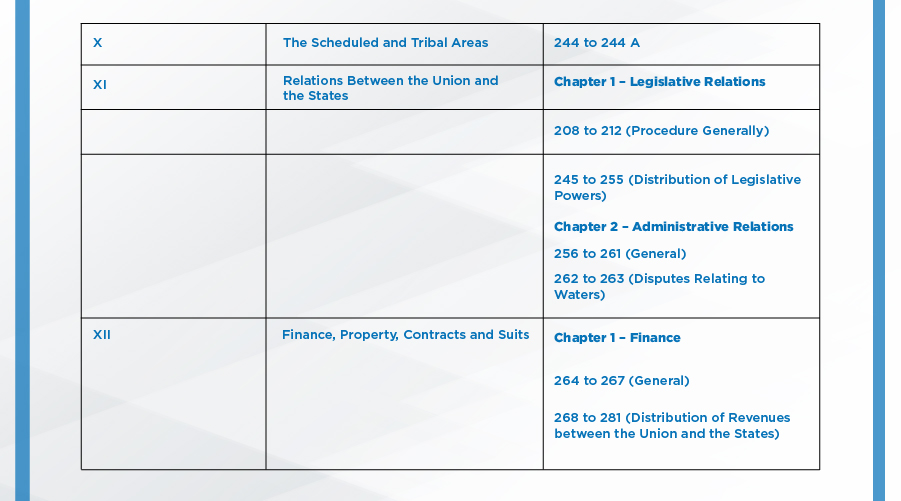

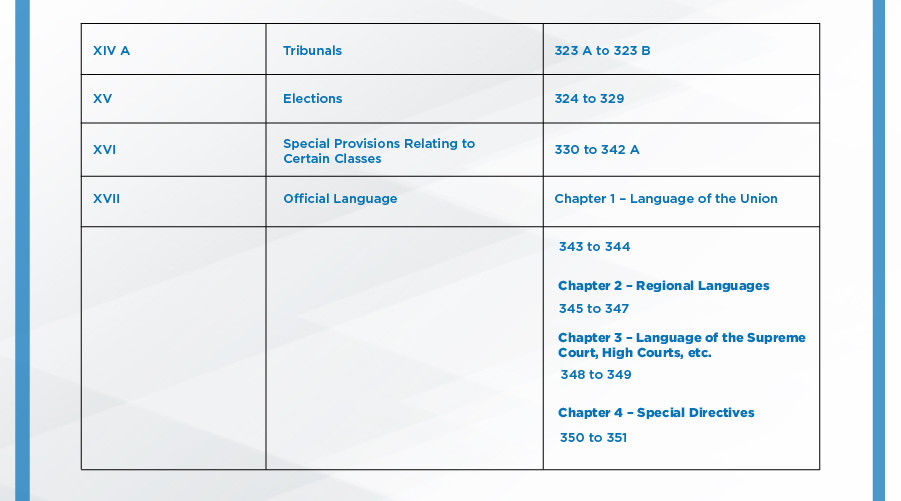
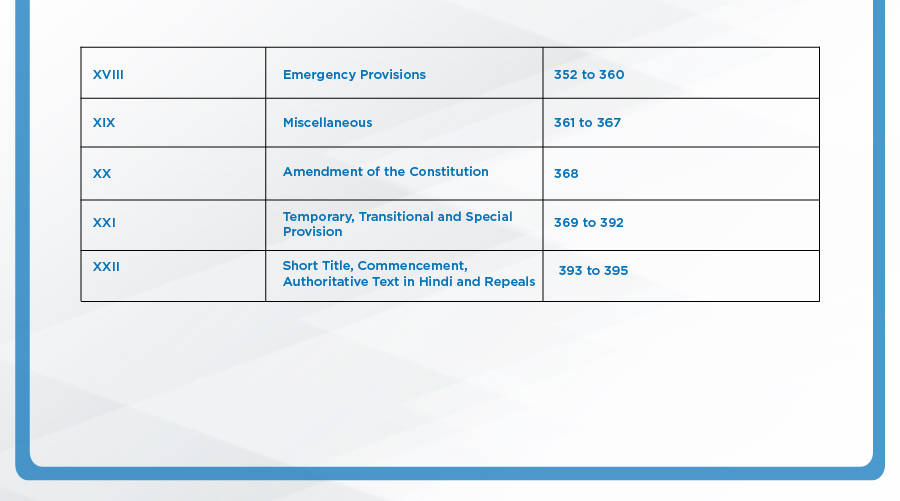
The Indian Constitution had 8 schedules originally, 4 more were added by different amendments, taking the total to 12: